What Is a Fixed Deferred Annuity
(When it comes to taxes, less is more.)

Last year, Americans purchased $125 billion worth of fixed annuities. No matter how you look at it, that's a ton of money. That's because fixed annuities have features that make them attractive to retirement savers, CD buyers, and retirees.
But there are 125 life insurance companies that sell fixed annuities in the US with hundreds of unique products. So how do you know what's right for you? Independent insurance agents are absolute experts when it comes to confusing puzzles like these. Their job is to simplify the process, guide you through all your options, weigh the good and the bad, and see you through it all from start to signature. Pretty nice, isn't it?
Let's Start at the Beginning: What's a Deferred Annuity?
Simply put, deferred annuities are called deferred because they don't pay an income to the owner right away. Deferred annuities have two phases, accumulation and payout. During the accumulation phase, purchase payments made by the owner grow tax-deferred. Then, during the distribution, or payout, phase the accumulated money is converted into a stream of guaranteed retirement income.
How Deferred Annuities Work
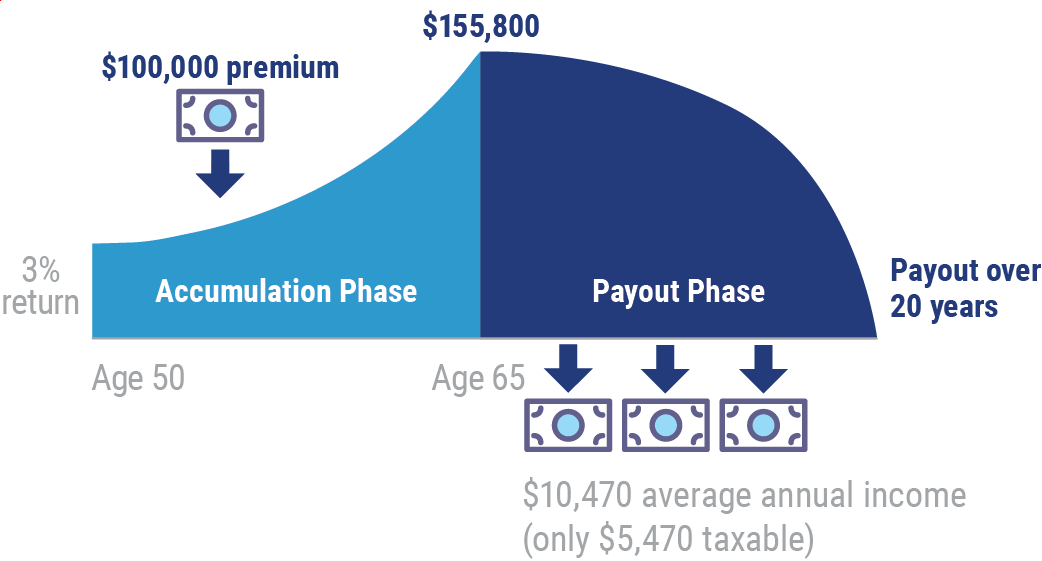
Deferred annuities are qualified or non-qualified. Qualified annuities are part of a pension plan or IRA. They’re purchased with before-tax dollars. Non-qualified annuities are personally owned and paid for with after-tax dollars.
What Is a Fixed Deferred Annuity?
The reason why fixed deferred annuities are called fixed is a bit confusing. The value of fixed deferred annuities is measured in dollars. When the value of the annuity rises or falls, it's because there are more or fewer dollars in the account. The value of variable annuities is represented by units. The value of each unit rises and falls with the investment it represents. The account value of a variable annuity changes based on the value of the units, not because there are more or fewer units.
That said, here's the part that really matters. Fixed deferred annuities guarantee principal. Once interest is paid, it's credited to the annuity account value and can't be taken away or lost. When fixed annuities pay income, the amount of income is guaranteed. Annuities, though, are not backed by the FDIC like CDs. The guarantees are only as strong as the insurance company's financials.
,
MYGAs offer a rate of interest guaranteed for a set number of years. Typically, buyers can choose from a 1 , 3, 5, 7 or 10-year rate with interest credited annually. MYGAs will typically offer rates that are higher than CDs. At the end of the guarantee period the insurance company will reset the rate.
Fixed Indexed Deferred Annuities
Fixed indexed annuities also guarantee principal. Instead of offering a rate of interest, the insurance company credits the account value based on the gains of a financial index, like the S&P 500. The gain cannot exceed the limit set by the insurance company, called a cap. If the index loses value, the account value remains the same. The advantage of a fixed indexed annuity is that the owner can benefit from the performance of the stock market without investment risk. The disadvantage is that the cap rates change each year, which affects performance.
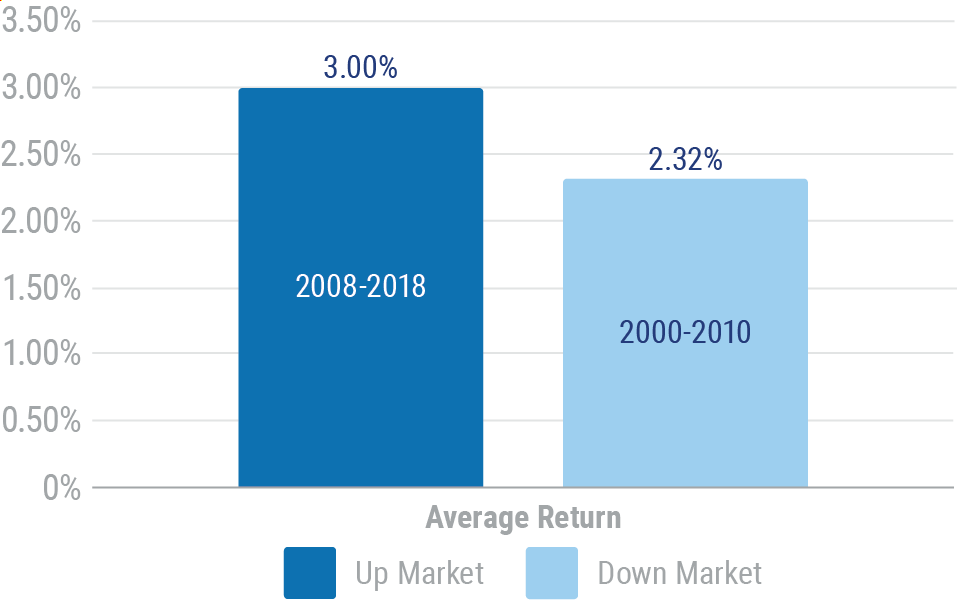
Fixed indexed annuities are measured by financial indexes, but shouldn't be compared to them. They more closely resemble their MYGA fixed annuity cousins. The chart below shows hypothetical results of an indexed annuity with a representative 4.25% cap measured by the S&P 500, excluding dividends, in a 10-year "up market" and a 10-year "down market".
Hypothetical 10-Year Performance of a Fixed Indexed Annuity Based on S&P 500 and 4.25% Cap
The Income (or Payout) Phase
A deferred fixed annuity may be converted to income at any time. There are several income options to choose from:
Life only. A payment is guaranteed for the lifetime of the annuitant. No payments are made after the annuitant's death. Life only options will pay out a higher monthly or annual income than the other options. Joint and survivor life only is available for the longer of two lives, usually spouses.
Life & period certain. Payments are guaranteed for the lifetime of the annuitant. The payments are made for at least a "certain" number of years regardless of when the annuitant dies. The certain year options are usually 10 and 20. Joint and survivor options are available for life and period certain.
Fixed period. Payments are made for a specified number of years regardless of when the annuitant dies.
What Are the Pros of Fixed Deferred Annuities?
Tax deferral. Fixed annuities offer tax-deferred growth. Unlike a CD or savings account, interest is not taxable until it is distributed, or withdrawn, from the annuity.
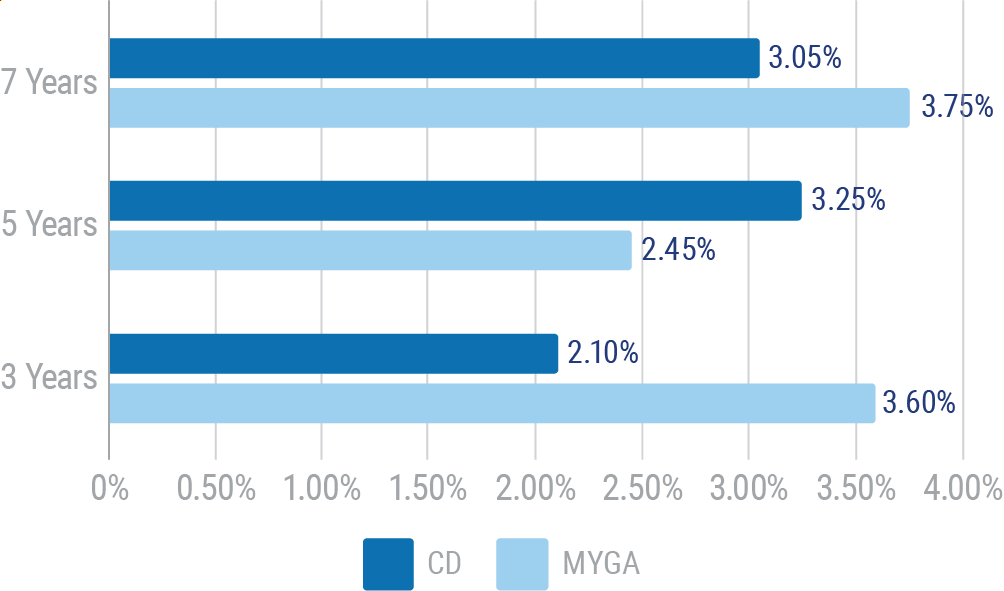
Higher rates of interest. Fixed annuities usually pay higher rates of interest than CDs or savings accounts. The chart below shows an example of MYGA rates available vs. CD rates.
Guaranteed lifetime income. Fixed annuities can pay an income guaranteed to last for life. Of all the concerns impacting retirement for Americans today, running out of money, maintaining their lifestyle, and rising healthcare expenses continue to top the list, according to the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Personal Financial Planning Trends Survey.
Creditor protection. Some types of assets can be protected from lawsuit judgments or bankruptcy. For some people who may be pmore likely to be sued (think doctors, corporate executives, etc.), protecting their assets from creditors can be a very important reason to buy a fixed annuity. Most states offer annuities some form of creditor protection. Some states protect all of the annuity proceeds from creditors, where others just protect the beneficiary's interest.
What Are the Cons of Fixed Deferred Annuities?
Tax penalties. There is a 10% tax penalty for any withdrawals before age 59-1/2.
Access to account values. Typically only 10% of the account value is available without penalty during the surrender period. Deferred annuities used for collateral may trigger immediate tax consequences.
Surrender penalties. Most fixed annuities charge a fee if you cash in your contract or withdraw more than 10% of the cash value. Surrender penalties decline to 0 over a period of years, usually not more than 10. MYGA surrender periods should match the guarantee period.
Market value adjustments/ The insurance company pays a fixed rate of return and absorbs any market risk. If you cash in your contract early, the insurance company loses money if interest rates are rising. The insurance company profits if interest rates are declining. The market value adjustment will be a cost or a bonus depending on interest rates.
What Happens If the Insurance Company Goes Bankrupt?
Insurance companies that sell fixed annuities are regulated by each state's insurance department. The state insurance departments have financial standards for licensed companies. Each state has guarantee funds to reimburse policyholders if the insurance company fails. The limits for each state are different.
Financial ratings of insurance companies are available from A.M. Best, Fitch, Moody’s and Standard & Poor.
| Highest Ability to Meet Obligations |
Medium Ability to Meet Obligations |
Lowest Ability to Meet Obligations |
|
| A.M. Best | A++ to A- | B++ to B- | C++ to C- |
| Moody’s | Aaa to Aa | A to Baa | Ba to Caa |
| S&P | AAA to A | BBB to B | CCC to C |
| Fitch | AAA to AA- | A+ to BBB- | BB+ to CC |
Is a Fixed Deferred Annuity Right for You?
Fixed deferred annuities are financial tools designed for retirement savings, and ultimately, lifetime income. Whether they're right for you depends on the job you want them to do.
Fixed deferred annuities are conservative investments. There's no market risk to them, but they are guaranteed by the insurance company, not the FDIC. If you're looking for a tax-deferred alternative to CDs, a fixed deferred annuity may be a good option.
Fixed annuities have limited access to account values during the surrender period. There are tax penalties for distributions before age 59½. They're not a good choice if you need access to the money for emergencies or other purposes.
What's So Great about Independent Insurance Agents?
Nobody ever said annuities are easy. Because the truth is, they aren’t. Now, they are a very beneficial and flexible financial tool, but they’re complex. Searching through the different options can be confusing, time-consuming and frustrating. An independent insurance agent's role is to simplify the entire process and show you the way.
They'll make sure you get the right product that meets your unique needs and will break down all the jargon so you understand exactly what you're getting.
Advisor’s guide to annuities John Olsen
Fundamentals of Investments Wilson & Hopkins
NAIC Buyers guide to deferred annuities
NAIC Statistical Report Life And Annuity Companies 2018
IRS PUB 575
IRS PUB 410
Fitch Ratings Definitions
Moody’s Moody’s rating scale and definition
S&P Global Understanding Ratings
A.M. Best Why An A.M. Best Financial Rating Is Important
The American College of Trust and Estate Counsel State Survey of Asset Protection Techniques
Gainbridge Life 3,5 and 7 year MYGA rates as published 1-16-2020
Marcus Bank and Suncoast Credit Union 3 and 5 year CD rates available 1-16-2020