Non-Qualified Variable Annuities & Taxes
(How Uncle Sam gets his share)

Neel Lane is an independent contract paralegal who specializes in Medicaid and VA benefits. He helps people access and maximize the benefits that they're entitled to. He has over 30 years of experience in this area.

Uncle Sam wants us to save for retirement. That’s why variable annuities have special features and tax benefits. Where there are tax benefits, there are usually strings attached. And annuities are no exception.
Our independent agent matching tool will find you the best insurance solution in your area. Tell us what you're looking for and we'll recommend the best agents for you. Any information you provide will only be sent to the agent you pick.
So what exactly is Uncle Sam’s share of your non-qualified variable annuity?
First Things First ... What’s an Annuity?
Annuities are policies issued by insurance companies that pay a regular guaranteed income for life or for a period of years. You buy an annuity policy by making either a single payment or a series of payments.
Deferred annuities accumulate money for a period of time before the policy pays income.
Immediate annuities start paying income right away.
Qualified variable annuities are part of pension plans, or IRAs. Qualified annuities that are part of traditional pensions and IRAs are purchased with before-tax dollars. Qualified annuities that are part of a Roth IRA or pensions are purchased with after-tax dollars.
Non-qualified variable annuities are personally owned and paid for with after-tax dollars.
Owners, Annuitants, and Beneficiaries
An annuity policy is a contract between the insurance company and these folks: The owner has the sole right to the values and payments in the contract and the owner decides who the annuitant and beneficiaries are.
The age and sex of the annuitant is how the insurance company determines how much and when income is paid. The annuitant and owner don't have to be the same person. The beneficiary receives the proceeds at the death of the owner or the annuitant.
The insurance company issues the policy and has to honor the promises in it. Guarantees in the policy are only as good as the financial ability of the insurance company to pay claims.
Terms You Need to Know
Gain: This is the total value of the account less purchase payments.
Annuity income: This is income taken under one of the insurance company’s annuity options. There is no access to principal once the option is selected.
Exclusion ratio: This is the percentage of annuity income that is not taxable as a return of principal.
Deferral stage: The period when the annuity is accumulating money.
Income stage: The period when the owner is receiving income.
Taxes During the Deferral Stage
Taxes follow some simple rules while the non-qualified variable annuity is accumulating money:
- No taxes are paid until distributions are taken.
- All distributions are taxed at ordinary income rates. Annuities are not eligible for capital gains treatment. Withdrawals of money, loans, and surrenders are all considered distributions.
- Withdrawals, loans, and surrenders are taxed as gain first.
- There is a 10% penalty on any distributions before age 59 1/2.
- The charts below show examples of how a withdrawal is taxed.
Eighty percent of $25,000 withdrawal taxed as gain at ordinary rates
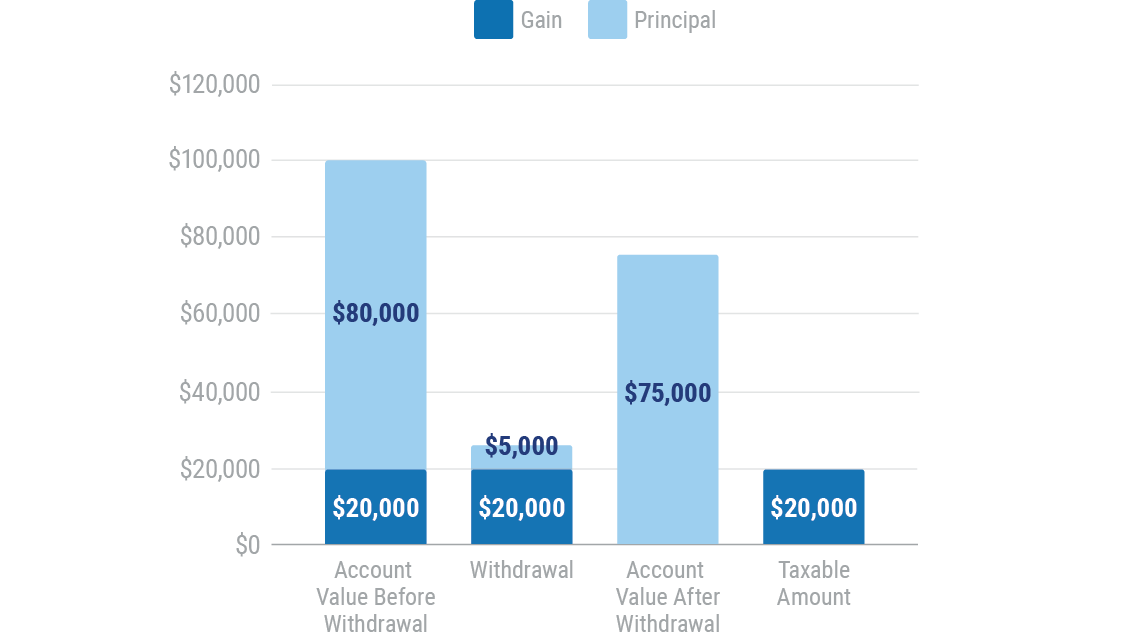
One hundred percent of $20,000 withdrawal taxed as gain at ordinary rates
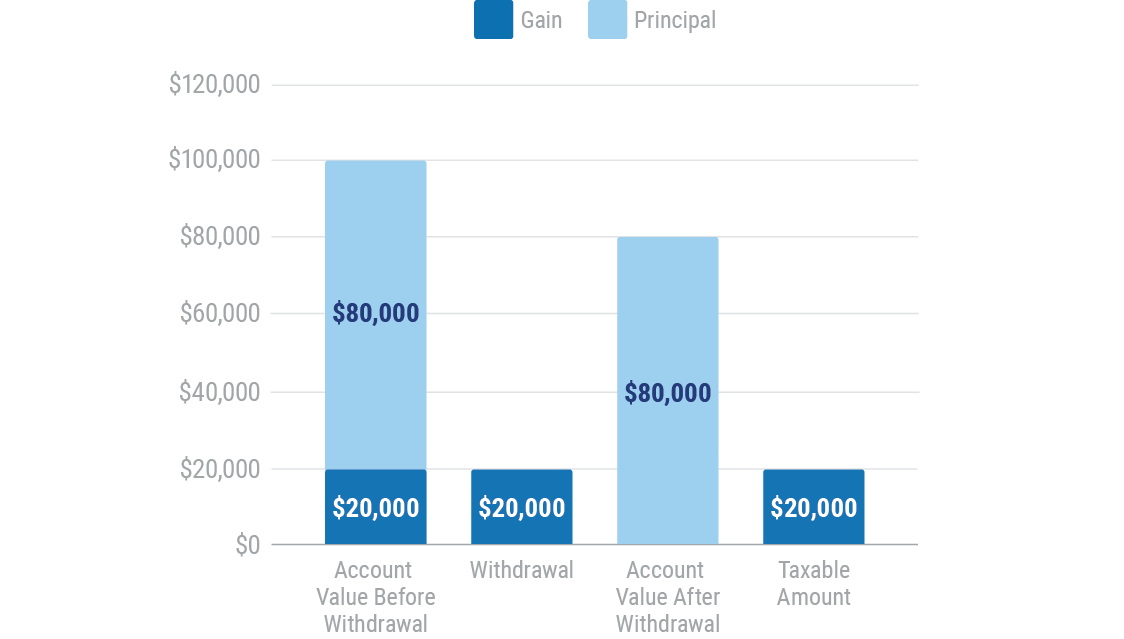
Taxes During the Income Stage
There are two ways to get income from a non-qualified variable annuity — withdrawals and an annuity option. Withdrawals are taxed the same way they are during the deferrals stage — gains first at ordinary income rates
Annuity income is taxed more favorably. A portion of the income is considered a return of principal. That portion is excluded from income tax and the balance of the payment is taxed at ordinary rates.
Pretty simple so far? Well not so fast.
Taxes on Your Legacy
Non-qualified annuities can be a way to plan for retirement income and leave a legacy for beneficiaries. The taxes due depend on whether the annuity was in the deferred or income stage at the time of your unfortunate demise.
The good news is that your beneficiaries have choices that can save them tax dollars. The bad news is that they have to pay tax at ordinary income rates on the gain.
What Happens if You Die During the Deferral Period
Uncle Sam doesn’t want to let the proceeds sit in a tax-deferred account forever. The rules are that annuity death benefits must be distributed at the death of the owner.
If you are a surviving spouse, you can take ownership of the annuity, including any riders and death benefits, within one year of your spouse's death. There is no income tax due until distributions begin.
Other options for beneficiaries are:
Five-year deferral: Able to take up to five years from the owner's death to withdraw the inheritance. Taxes are not due until withdrawals are taken. The money will continue to accumulate tax deferred.
Lump-sum distribution: Taxes are due immediately.
Stretch distribution: The distribution is taken as a percentage over time. Taxes are due as you receive the payments. The distributions may be partially or fully taxable.
Annuitization: The assets are converted into income. The payments will be partially taxable according to an exclusion ratio.
Your beneficiary can decide what option to take based on their immediate needs and tax situation.
What Happens if You Die During the Income Period
Any remaining payments to the beneficiary will be taxed the same way as to the owner. The same options as the deferral period are available for any remaining values such as refunds.
The Bottom Line
Non-qualified variable annuities are financial tools that offer tax-deferred growth, and in some cases tax-deferred income. Be sure to consult your professional advisor for tax and legal advice.
Use our independent agent matching system to find the best insurance plan in your area. You tell us what you’re looking for, and our technology will recommend the best agents for your needs. Any information you give us will only be sent to the agents you pick.
The advisors Guide To Annuities John Olsen
IRS Publication 575
